Male Reproductive Organs
The main task is to produce, store, transport and orgasm and ejaculate sperm.
External Reproductive Organs:
There is the penis and the scrotum containing the testicles.
Internal Reproductive Organs:
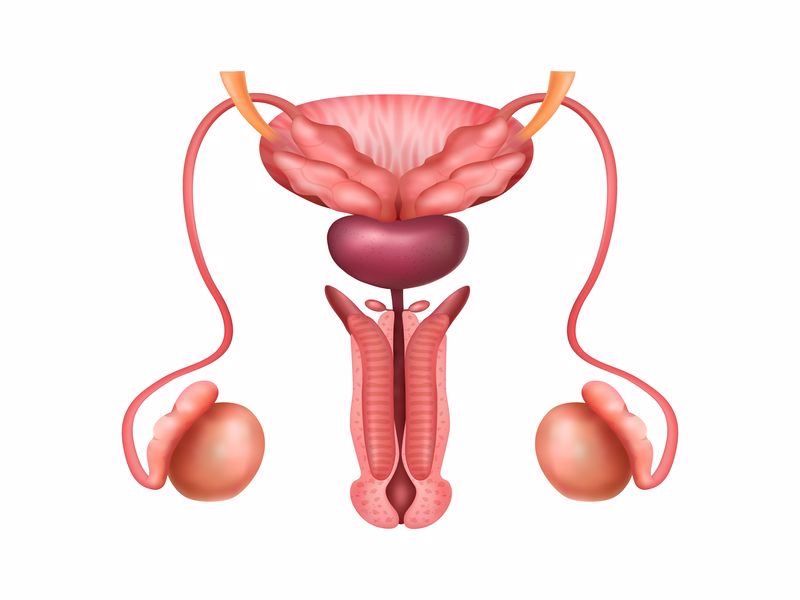
Penis:
It is a spongy, nearly 5-12 cm long, 3-5 cm thick, porous organ with blood vessels, consisting of a head (glans) and body (corpus). In the case of an erection, the pores fill with blood and the penis becomes hard and enlarged. The head of the penis is the most sensitive and erogenous part of the penis, thanks to its rich nerve endings. In uncircumcised men, this part is covered with a skin called the preputium.
A thin space extending from the bladder to the outlet at the tip of the glans extends from the inside of the body, and this space is called the urethra. It is the channel where semen and urine are excreted in men. It is long in men, so they are less likely to have a urinary tract infection than women.
Testicles (Hayas):
It is two. It is located in the testicular sacs. In this way, they are protected from high heat in the body. Average weight of 30 grams, 4-5 cm in length.
With the effect of the pituitary gland, which produces the hormone FSH in the brain, sperm cells are produced from Sertoli cells by means of convoluted tubules called seminiferous tubules in the testicles. With the effect of LH hormone produced from the
pituitary gland, Testosterone hormone is produced from Leydig cells in the testis. Testes are endocrine organs because they produce hormones.
The testosterone hormone is responsible for the secondary sex character in adolescence (such as deepening of the voice, male-pattern hair growth, sperm formation and development, muscle development, etc.).
In the intrauterine life (in the womb), in the presence of the Y chromosome and thanks to the production of Testosterone, the internal and external genital organs develop in the male direction and a male baby is born.
Sperm Formation (Spermiogenesis):
How does sperm production occur? What is sperm made of?
Sperm cells in the testis (sexual reproductive organs) are formed from spermatogonia with 2N chromosomes in the seminiferous tubules, with meiosis, sperm cells with 23 chromosomes and an X or Y chromosome are formed. This is called spermatogenesis. This process is regulated by many hormonal and paracrine factors. Sperm completes the development process in about 70 days.
Sperm production is continuous, produced, stored and discharged. During fertilization, if the Y chromosome fertilizes the egg, the baby is born as a boy, if the X chromosome fertilizes the egg, the baby is born as a girl (except in special circumstances).
Epididymis:
It is the structure that carries the sperm between the canals in the testis and the structure called the vas deferens (seed canal) and serves as storage and maturation. It is just above the testis. It is 5-6 cm long. Contractions during sexual arousal push the sperm into the vas deferens.
Vas Deferens:
It is in the form of a two-sided tube with a length of 40-50 cm. At the base of the prostate, the seminal vesicle joins with the excretory duct and participates in the formation of the ejaculatory duct.
Ejaculatory Channels:
It is the 2 cm section after the vas deferens merges with the drainage channel.
Urethra (Urinary Tract):
It extends from the bladder to the tip of the penis. In the case of an erection, the flow of urine is blocked and ejaculation occur.
Seminal Vesicles (Vesicles):
It is between the base of the bladder and the rectum. It is 5-7cm long, 2.5cm wide. The gland consists of convoluted ducts. The fluid that protects the sperm from the acidic environment of the vagina is secreted from these vesicles, whose secretion is regulated by testosterone. 60% of the semen consists of this fluid, which is rich in mucus, protein and fructose.
Prostate Gland:
Located under the bladder, the urethra runs through the center of the prostate gland.
Semen is called the liquid that contains sperm in the ejaculate. It is an opaque-gray colored liquid with a volume of 1-5 cm, with a specific odour. 20% of the semen is composed of fluids coming from the prostate.
The first liquid coming from the penis during ejaculation consists of those coming from the prostate, the sperm is dense and it is called pleasure water.
All these fluids nourish the sperm and increase its movement, protecting it from external factors.
The semen remaining outside after ejaculation becomes liquefied and melts. Approximately 150 million sperm cells are expelled during one ejaculation.
Bulbourethral Glands (Cowper's gland):
It is below the prostate gland and opens directly into the urethra, producing an alkaline fluid. The ejaculation thin flows into the urethra with sexual arousal.
You May Also Interested In
The biggest difference in the anatomy of men and women is in the genital organs.…
Read more




