Laparoscopy is a technique widely used today for surgical interventions and diagnosing certain diseases. It involves using a special camera and surgical instruments inserted through several small incisions in the abdominal cavity. This allows doctors to closely examine internal organs, make accurate diagnoses, or perform precise surgical procedures.
What is Laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy, particularly valuable in diagnosing and treating abdominal diseases, is also known as "minimally invasive" or "keyhole" surgery. The procedure is performed through incisions of 1 cm or smaller, through which instruments are inserted. A camera provides real-time imaging on a monitor, allowing the surgeon to see inside the abdomen.
Compared to open surgery, laparoscopy causes less trauma to the patient, making it a preferred choice. Laparoscopy can be used both to detect abnormalities within the abdominal cavity and to treat them. With the help of devices called laparoscopes, the procedure minimizes the risk of complications, accelerates the patient's recovery, and leaves minimal scarring.
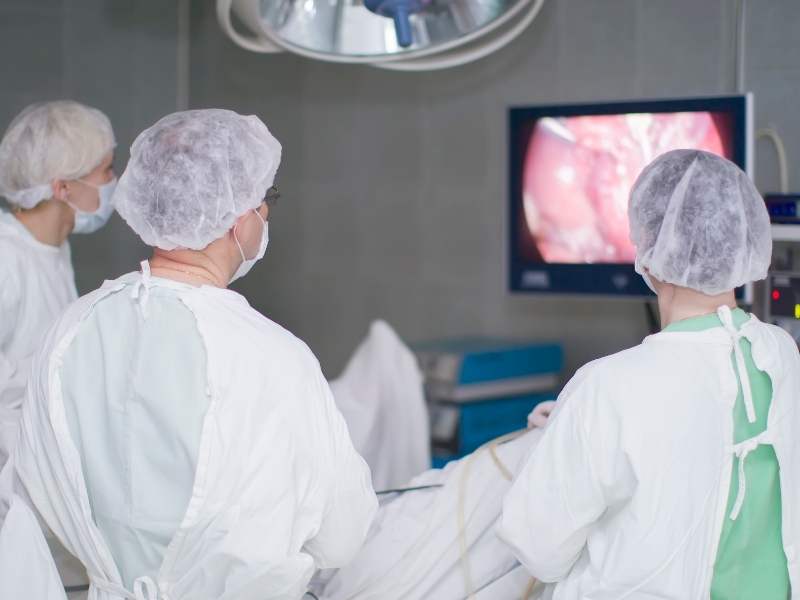
Why is Laparoscopy Performed?
Laparoscopy is widely used in treating suitable conditions due to its numerous advantages. When aiming to minimize post-surgical risks, laparoscopy is often the preferred technique. It is especially common in diagnosing and treating gynecological conditions.
Laparoscopy also facilitates accurate diagnosis of certain conditions. It can be highly effective in diagnosing endometriosis, ectopic pregnancy, ovarian cysts, and similar issues.
How is Laparoscopy Performed?
Laparoscopy is conducted under general anesthesia. A small incision is made in the lower abdomen, through which carbon dioxide gas is introduced to inflate the abdominal cavity, allowing better visibility of the internal organs.
The laparoscope is then inserted through minimal incisions on the abdomen. The camera on the end of the laparoscope transmits images to a monitor, providing the doctor with a clear view of the abdominal organs.
The number of incisions made during laparoscopy depends on the condition being treated. Once the procedure is completed, the instruments are removed, and the incisions are closed.
Types of Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is used in treating a variety of conditions, especially in gynecology. Common types of laparoscopy for women’s health include:
- Laparoscopic cyst removal
- Laparoscopic myomectomy (fibroid removal)
- Laparoscopic hysterectomy (removal of the uterus)
Advantages of Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy offers several advantages over open surgery. It provides greater comfort for patients and simplifies the recovery process, benefiting both patients and doctors.
Key advantages of laparoscopy include:
- Reduced Pain and Discomfort: Patients experience less pain compared to open surgery.
- Lower Risk of Infection: The smaller incisions decrease the likelihood of infection.
- Faster Recovery Time: Patients typically recover more quickly.
- Smaller Scars: The minimal incisions result in smaller scars.
- Less Tissue Damage and Blood Loss: With fewer and smaller incisions, there is less tissue damage and reduced blood loss.
- High-Resolution Imaging: The advanced camera system provides clear views of internal organs.
- Minimally Invasive: The small incisions required for laparoscopy make it a less invasive procedure.
These advantages make laparoscopy a preferred choice for both patients and healthcare providers.

For Which Conditions is Laparoscopic Surgery Used?
Laparoscopic surgery is applied in the treatment and diagnosis of various conditions. Common uses include:
- Removal of fibroids
- Hysterectomy (removal of the uterus)
- Tubal ligation (tying the fallopian tubes)
- Endometriosis surgery
- Treatment of ectopic pregnancy
- Diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cysts
- Identifying causes of infertility
- Diagnosing abdominal pain
How Long Does it Take for Laparoscopy Incisions to Heal?
Laparoscopy incisions typically heal within a week, allowing most patients to return to normal activities in that time. Since the incisions are smaller than those made in open surgery, they heal faster and leave minimal, aesthetically small scars.
What are the Risks of Laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy carries lower risks than traditional open surgery, but as with any surgical procedure, there are some potential risks, including infection, bleeding, and bruising. Anesthesia may also cause side effects such as nausea and vomiting. While these risks are inherent to any surgery, they are quite low in laparoscopic procedures.




