Gynecological Diseases
Routine gynecological examinations are very important in the early diagnosis and prevention of gynecological diseases. Routine gynecological examinations should be performed starting from the first menstrual period.
Routine gynecological examinations should be performed once a year, even if the woman has no complaints. After starting an active sexual life or for every woman between the ages of 18 and 65, it is very important for the early diagnosis and treatment of many gynecological diseases. Many diseases such as ovarian cysts, infectious sexual diseases, myomas and early-stage cancers can be detected with routine check-ups.
If you have any suspicion of pregnancy, abnormal vaginal bleeding, burning sensation during urination, foul-smelling or colored vaginal discharge, infection, or pain in the pelvic area outside of routine check-ups, you should consult your doctor as soon as possible.
What are Women's Diseases?
Women's diseases also include the female reproductive system, such as the ovaries, vagina, cervix, and fallopian tubes, also known as gynecological diseases. In women's diseases, menstrual problems, sexuality, infertility, menopause, and birth control are diagnosed and treated. In some cases, women's diseases cannot be noticed, but are detected only with routine examinations. Gynecology and obstetrics specialist Assoc. Prof. Dr. Çiğdem Yayla Abide provides examination, diagnosis, and treatment services in the gynecological field.
The Most Common Women's Diseases
The most common women's diseases are menstrual problems such as painful menstruation or amenorrhea, polycystic ovary disease, vaginal discharge problems, and endometriosis, also known as chocolate cysts. When the symptoms of these diseases are seen, a specialist gynecologist should definitely be examined. Groin pain in women can be caused by many reasons, as well as a problem originating from the reproductive organs. The cause of groin pain can be a cyst in the ovary or an ectopic pregnancy. The most common women's diseases can be listed as follows.
- Menstrual irregularity
- Ovarian cyst
- Myoma
- Endometriosis
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- HPV
- Polyp
- Gynecological cancers
- Vaginal fungus
- Vaginal discharge
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Menopause
- Vaginismus
- Sexual dysfunction
- PMS or premenstrual syndrome


Treatment Methods in Gynecological Diseases
Treatment methods in gynecological diseases include different methods depending on the disease. Treatment methods include medication, alternative methods and surgical interventions. The appropriate treatment method is determined by the specialist doctor according to the patient's needs and the condition of the disease. Laparoscopic surgeries in particular are a suitable method for the treatment of many gynecological diseases. Laparoscopic surgery, known as closed surgery, is applied in the treatment of diseases such as endometrioma, myoma surgery, ovarian cyst, ectopic pregnancy, removal of fallopian tubes, and uterine cancer. Open surgery is performed more frequently in cases of high myoma count. HPV vaccination is recommended for HPV at a young age, and in the following periods, a smear test is taken once a year from people who have regular relationships. Cervical anomalies detected with a smear test are diagnosed early and treated before they turn into cancer.
What is Gynecological Examination?
Gynecological examination is a type of examination performed to evaluate a woman's gynecological health. With this examination, ovarian cysts, sexually transmitted diseases, and early stage cancer symptoms can be detected. Gynecological examination is an important stage that every woman should have routinely. For problems such as vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding, and vaginal fungus, gynecological examination is also important in terms of diagnosis.
Even women who are sexually active and even have children may have a fear of feeling pain during a vaginal examination. However, in order to understand that this fear is unnecessary; it is enough to know the structure of the vagina, the size and materials of the instruments used during the examination. The instrument called speculum, which is frequently used during a gynecological examination, is much thinner than the penis. On the other hand, a large amount of gel is applied to the vaginal ultrasound device or instruments such as speculum before entering the vagina. In this way, the instrument becomes lubricated and easily enters the vagina. Only the speculum, which is slightly opened to provide sufficient opening in the vagina, will create a feeling of pressure, and this is not a pressure strong enough to cause pain. Another instrument used is the smear stick used for the smear test. The brush-like structure at the end of the stick is extremely soft and does not contain any irritating materials.
How is an Obstetrics and Gynaecology Examination Performed?
After the doctor listens to your complaint and talks to you about your medical history, he/she requests that you go to a different room or a different section of the room for the gynaecological examination. Your doctor's assistant gives you a gown and asks you to take off your clothes and get ready. When you lie down on the examination table called the gynaecological table, you are now ready for the examination. The gynaecological examination is performed manually and with a sterile single-use tool called a speculum. Then, it ends with an ultrasound evaluation of the gynaecological organs. A rectal examination can also be performed if necessary.
The doctor first examines the vulva from the outside and examines if there are any symptoms such as wounds, swelling, redness. Then, he/she performs a vaginal examination using gynaecological instruments. There may be a slight feeling of discomfort during the examination, but no other pain is experienced. The examination takes approximately 10-15 minutes.
During the gynaecological examination, the following parts of the body are examined;
- Vulva (external genital organs)
- Uterus
- Cervix
- Ovaries
- Bladder


Routine Examinations That Women Must Have
A gynecological examination is an examination that all women should have from a young age and is very important in terms of early diagnosis of some diseases. We recommend that a smear test be taken from your cervix annually or at least every 3 years after your first sexual intercourse or at the age of 21, and that an HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) screening test be added to this test after the age of 25.
We recommend that you do your own breast examination in every bath, and that you have mammography and breast ultrasound at regular intervals after the age of 40. After the age of 50, we recommend that you have a stool occult blood test and a colonoscopy at certain intervals for early diagnosis and prevention of colon cancer.
What is Gynecology?
Gynecology is a branch of medicine that focuses on women's reproductive health, diagnosis and treatments in this field. Gynecologists provide services to protect women's sexual health, diagnose women's diseases and treat women's diseases. This is the department where women apply to obtain information about the issues they complain about and to have their annual routine examinations. Gynecological examinations can be scary for most women, but they are very important in order to solve the problems in your reproductive health and organs such as the vagina and uterus.
Things to Consider Before Routine Gynecological Examination
Since there is a possibility of a smear test being performed during the gynecological examination, it would be beneficial to schedule your examination time to coincide with the period after menstrual bleeding has ended, unless otherwise recommended by the doctor. Approximately 2 days before the gynecological examination, tampon use, sexual intercourse, any liquid, foam or gel substance squeezed into the vagina, cream or cleansing liquid applied for treatment purposes should be completely stopped.
For people who have never had sexual intercourse before, the doctor will choose the appropriate examination method. In these people, except for some cases, a vaginal examination is not performed, a rectal examination can be performed or the examinations can be completed with abdominal ultrasonography.

Curiosities About Menopause cover an important biological process that is a natural part of many women’s lives.
Read more
Uterine prolapse is the name given to the sagging of the uterus downwards from the point where it should normally be. The uterus, also defined as uterus in medical language, is between 5 and 6 cm in women who have not given birth, while in some women it is between 6 and 7 cm. It is located on the inside of the pelvis, behind the urinary bladder, in front of the intestines. It is an organ with limited movement ability. It can sag over time due to advanced age or excessive number of births.
Read more
Fibroids that develop on the muscle layer of the uterus are masses that can be seen in 20 out of every 100 women. The reason for the formation of these masses is not known exactly. Fibroids, which are generally benign, are seen in almost fifty per cent of women over the age of 50. Fibroids usually develop in more than one number. Treatment of fibroids can be done in different ways. Fibroid surgery is one of the treatment methods applied.
Read more
The exact cause of fibroids is unknown, although obesity is known to increase the risk. Fibroids form in the uterus but do not develop in the ovaries. They are more common after age 40 and occur in about 25% of all women. Fibroid treatment options are available, and surgical treatment is often preferred.
Read more
Vaginal yeast infections are common among women, with three out of four women experiencing it at least once in their lifetime. Vaginal yeast infections can affect women of all ages and are treatable.
Read more
Women's health is one of the most important issues that should be protected through regular gynecological check-ups. During these examinations, certain tests play a vital role in the early diagnosis of cervical diseases.
Read more
One of the most common uterine disorders in women, fibroids are usually benign but can cause serious problems such as pain, irregular bleeding, and fertility issues as they grow.
Read more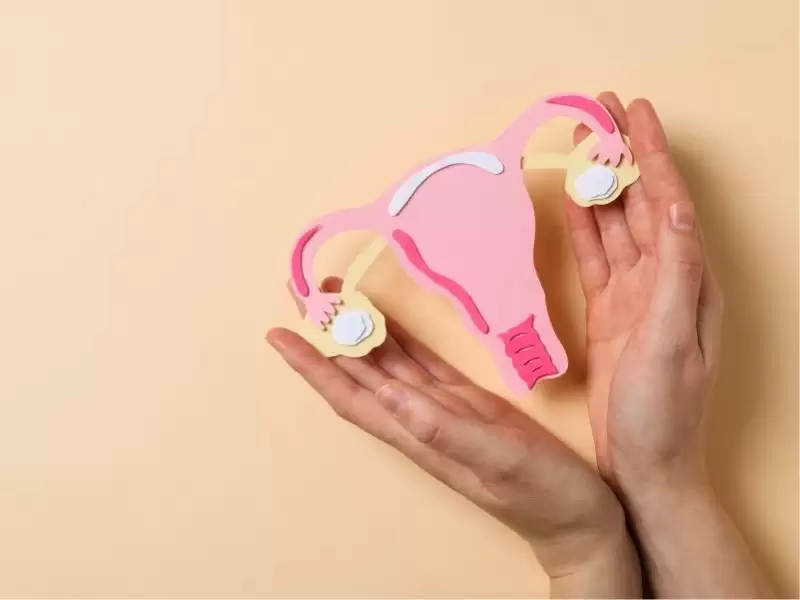
Progesterone is a sex hormone that plays a fundamental role in the female reproductive system. It is often called the “pregnancy hormone.
Read moreProf. Dr. Cigdem Yayla Abide
She was born in 1980 in Zonguldak. She completed her secondary and high school education at TED Zonguldak College with a degree and with her outstanding success in the university exam, she was entitled to receive medical education in English at Marmara University Faculty of Medicine. This is how she took the first step towards becoming the obstetrician and gynecologist she dreamed of. After graduating from the faculty of medicine, she obtained a high degree in the medical specialization exam (TUS) in 2007 and started to specialize in Zeynep Kamil Gynecology and Pediatrics Training and Research Hospital, which was her first choice. By working for many years in one of Turkey's leading, specialist hospitals; She has taken part in countless births and in the treatment of thousands of diseases. She worked at Nallıhan State Hospital between 2011 and 2014 in order to fulfill her obligatory duty of public service as a specialist physician.