Genital warts, a health condition affecting both men and women, are caused by the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). These warts can be transmitted through sexual contact and direct skin-to-skin contact. Fortunately, various treatment methods are available to manage genital warts.
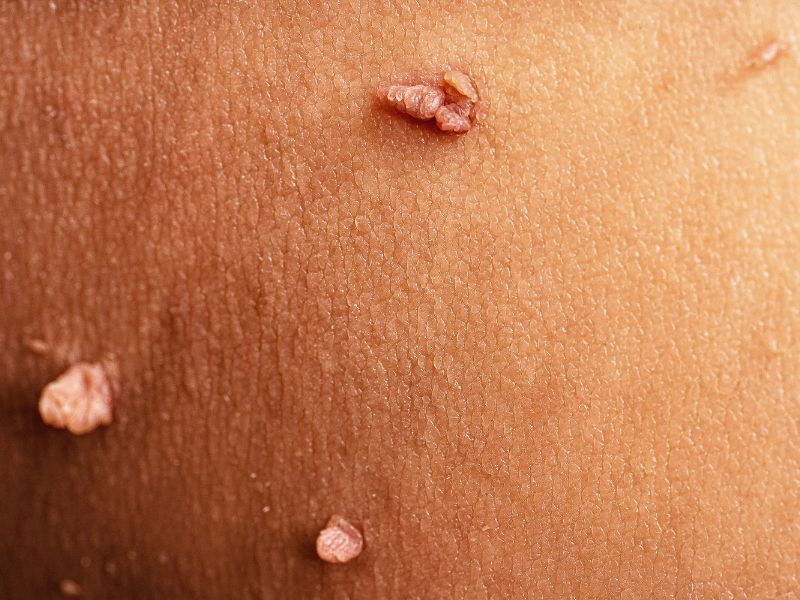
What Are Genital Warts?
What Are Genital Warts?
Genital warts are a type of wart caused by HPV, a virus transmitted through contact, with sexual contact being the primary transmission route. These warts, which may look like small skin-colored bumps or resemble cauliflower, are generally painless. However, some people may experience itching or discomfort. Genital warts are most commonly caused by HPV types 6 and 11, although there are hundreds of HPV strains, some of which can lead to more serious conditions, like cervical cancer. HPV types 16 and 18 are known to be high-risk strains associated with cervical cancer, while warts are typically caused by other, low-risk HPV types.
What Causes Genital Warts?
The main cause of genital warts is the HPV virus, which has over 40 strains known to specifically cause genital warts. While HPV types 6 and 11 are often the primary culprits, there are comprehensive tests available to identify the specific HPV strain causing the warts. The most common cause of genital warts is unprotected sexual contact with someone who has the infection. Although rare, genital warts may also spread through contact with shared, damp surfaces, such as public toilets or pool lounge chairs. Factors that increase the risk of genital warts include having multiple sexual partners, engaging in unprotected sex, starting sexual activity at a young age, and having a weakened immune system that cannot effectively fight off HPV.
Types of Genital Warts
There are various types of genital warts, and specific testing can identify which type of HPV is present. Genital warts may differ in appearance depending on the HPV strain and location on the body. Some common types include:
- Condyloma Acuminata: The most prevalent type, usually caused by HPV types 6 and 11, appearing as flat or cauliflower-like growths.
- Papular Warts: These warts are skin-colored or white and may appear around the anus, on the penis, or at the vaginal opening, often in clusters.
- Flat Warts: Generally smooth in appearance, flat warts may develop on the vulva or the tip of the penis.
- Keratotic Warts: These are thick and hard, commonly appearing around the anus and on the penis.
- Internal Warts: Often found in the cervix, anal canal, or vagina, these warts are usually painless and not visible externally.
If you experience symptoms or suspect HPV infection, consulting a healthcare provider is essential to diagnose and manage the condition appropriately.
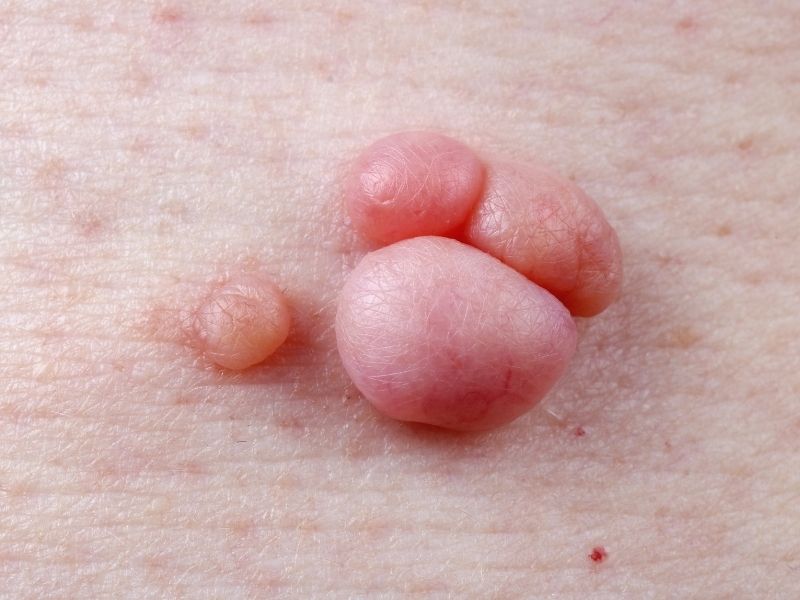
Genital Wart Symptoms
Genital Wart Symptoms
Genital warts often do not present symptoms, but in some individuals, symptoms may appear. Genital wart symptoms include:
- Raised skin-colored growths
- Cauliflower-like flesh protrusions
- Itching and discomfort in the genital area
- Sensation of pain
- Mild bleeding during or after sexual intercourse
How to Treat Genital Warts
For genital wart treatment, it is essential to first examine the location and extent of the wart spread. If the lesion is large and widespread, surgical intervention may be necessary. For warts that affect a smaller area, cauterization and laser treatments can be used to burn off the lesion. Cream treatments are also available for genital warts, but these creams differ from those used on other body parts and should not be applied without a doctor’s prescription. Wart treatment is available at Doç. Dr. Çiğdem Abide’s private clinic in Istanbul. You may contact the clinic for information on wart treatment in Ataşehir.
Do Genital Warts Recur?
Genital warts may recur as they stem from the HPV virus present in the body. Keeping immunity strong, maintaining a healthy diet, and exercising may help prevent HPV from causing warts. Receiving HPV vaccinations, which offer protection against nine types of HPV, may also reduce the likelihood of genital warts recurring, even if the person has already contracted HPV.







