"The egg freezing process is applied recently due to the advancing age or the possibility of ovarian damage, in order to freeze women's eggs and use them later for in vitro fertilization. It is a method preferred by women who postpone having children due to any illness or who plan their careers and want to become mothers at an older age."
With the egg freezing method, women can use their eggs in the future. The egg freezing method enables a woman to ensure that she can have children later on. The main purpose here is to preserve a woman's fertility. One of the prominent features of the procedure is that the egg cell maintains its biological structure from the day the procedure is performed. It is said to be a process that allows women to become mothers at an older age. It is deemed suitable for those who cannot get pregnant under current conditions or present risks. Additionally, it is known to be a very suitable method for those who wish to become mothers in the future. It has also been observed that it is a method that has recently emerged and is quite curious for many people.
What is Egg Freezing?
With this method, women are offered the opportunity to conceive at an older age. Due to certain diseases, risks, or existing conditions, some women cannot become mothers. However, thanks to this method, their eggs are frozen, allowing them the opportunity to become mothers in the years to come. It has also been observed that this method has made significant progress in the last 50 years. Moreover, it is known to be a procedure that takes a relatively short time. It is applied to patients deemed suitable. Therefore, the reason for the person's desire for this method is first listened to, and they undergo certain examinations in this regard. As a result, a decision is made on whether or not to apply the procedure.
Why Is Ovarian Tissue Freezing Done?
Ovarian tissue freezing preserves reproductive options for those who may wish to become pregnant in the future.
- Women with declining ovarian reserves,
- Those who will undergo chemotherapy or radiotherapy,
- And those with low AMH levels or diminished ovarian reserve should be informed about ovarian tissue freezing.
Who Can Undergo the Egg Freezing Procedure?
To be eligible for the egg freezing procedure, a person must first undergo a thorough examination to assess their symptoms and circumstances. Based on the examination, it is determined whether egg freezing is appropriate for the individual. Those who may qualify for egg freezing include:
- Individuals who have reached puberty,
- Those with a family history of early menopause,
- Those who do not plan to become pregnant before the age of 38 due to life plans,
- Individuals with low ovarian reserves,
- Those currently undergoing or soon to undergo radiotherapy or chemotherapy,
- Individuals who have had or will undergo surgery on reproductive organs.
How Is the Egg Freezing Procedure Performed?
First, specific tests are conducted on the individual undergoing egg freezing. A detailed examination is carried out through ultrasound and blood tests, along with essential assessments to detect any underlying health conditions. If the patient's circumstances are suitable, they are advised to start taking certain medications on the second or third day of their menstrual cycle. These medications aim to stimulate egg production. Injections and ultrasound examinations are typically carried out daily over an average period, with close monitoring to adjust procedures as necessary. Once patient consent is obtained, documentation specifying the reason for the freezing procedure is added to the patient’s file.
The treatment begins similarly to the in vitro fertilization (IVF) process. Hormone therapy is started to promote the growth of eggs, with ultrasound and hormonal monitoring to track the follicles in the ovaries. When the eggs reach a size of 18-20 mm (usually within 10-11 days), a trigger injection is administered to mature the eggs. Approximately 34-36 hours later, the eggs are retrieved through an OPU (Oocyte Pick-Up) procedure and handed to embryologists. The mature eggs collected are then frozen using a rapid freezing method known as vitrification. They are stored in storage tanks containing liquid nitrogen at -196 degrees Celsius, where they can be preserved for years (with comprehensive records maintained for all samples).
How Are Eggs Frozen?
After the eggs are collected, only the healthy and mature ones are selected. Following a brief preparation period under specific conditions, the freezing process is carried out using a rapid freezing technique. The eggs are then stored at -196 degrees Celsius, with primary attention given to preserving their biological properties. Under controlled conditions, eggs can be preserved for over five years.
What Is the Importance of Egg Freezing?
Today, many women are postponing childbearing due to career considerations. However, studies and experience show that younger age is a critical factor for achieving a healthy pregnancy, either naturally or through IVF. Egg freezing becomes highly relevant in this context, allowing women the option to preserve their fertility. Egg freezing can also be performed at later ages, and the eggs can be thawed whenever desired to attempt pregnancy. Additionally, for cancer patients about to undergo chemotherapy, eggs can be frozen and stored before treatment begins.
Are Babies Born from Pregnancies Achieved Through Egg Freezing Healthy?
The first twin pregnancy using frozen eggs occurred in 1986. There is no evidence in the medical literature suggesting that babies born from frozen eggs are unhealthy. Today, many women postpone childbearing due to reasons such as career planning, education, work commitments, not being ready for a second child, or health issues. The number of live pregnancies achieved through thawed frozen eggs is steadily increasing, which has led to a rise in demand for egg freezing over the years.
The chance of conception in women is highest in their mid-20s, but declines significantly after age 35. As age increases, egg quality decreases, and chromosomal issues in the eggs may emerge. Consequently, in later-age pregnancies, the risks of giving birth to a baby with anomalies or experiencing a miscarriage are higher.
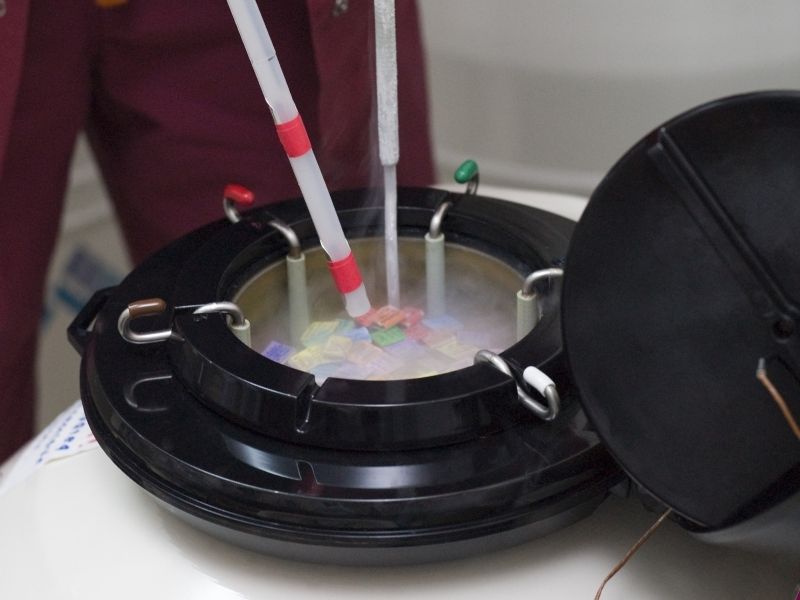

Is Egg Freezing Safe?
The number of eggs being thawed and used each day continues to grow, and live birth rates are increasing as well. Research shows that even when eggs are thawed 15-20 years later, live births can still be achieved. Studies indicate that with today’s technology, embryos created from thawed frozen eggs, when used in IVF treatments, have live birth rates comparable to those created from fresh eggs.
There has been no observed increase in the risk of anomalies or other problems in babies born from frozen eggs, indicating that egg freezing is a safe method.
What Are the Innovations in Egg Freezing?
Currently, only mature eggs can be frozen after retrieval. However, with a recent technique known as IVM (In Vitro Maturation), immature (GV) eggs can also be collected, matured in the lab, and then stored.
Ovarian tissue (or ovarian cortex) can also be frozen today. However, this method has some disadvantages. It requires a surgical procedure, and if there are cancerous cells in the ovarian tissue, there is a risk that malignant cells could be reintroduced to the patient when the tissue is transplanted back.
Is DNA Identification Mandatory?
Before storing eggs, a blood sample is taken from the woman in an EDTA tube and preserved under suitable conditions. DNA identification tests are conducted on this blood sample prior to storage. This information is placed in the patient’s file, with a copy also given to the patient. If the storage period exceeds one year, the patient must submit a signed statement affirming continued consent.
Does the Age at Which We Use the Eggs Affect Pregnancy?
Regardless of the age at which the eggs are used, the key factor is the age at which the eggs were collected and frozen. Eggs frozen at a younger age retain their “youth” when thawed, leading to higher chances of success in IVF treatments. The earlier eggs are frozen, the greater the success rate, with live birth rates reaching as high as 70%.
What Determines Success in Egg Freezing?
First, it’s important to clarify what “success” means in egg freezing procedures. Success refers to the survival of the eggs after thawing, with studies indicating a survival rate of around 80-90%. The ultimate measure of success, however, is the live birth rate, which ranges from 40-70%.
The most significant factors affecting success are the woman’s age and the number of eggs collected. The younger the woman and the greater the number of eggs retrieved, the higher the likelihood of success.
Other factors include the technology used, the egg freezing method (the vitrification technique, or rapid freezing, is more effective than slow freezing), the experience of the embryologist, the quality of the laboratory, the expertise of the gynecologist (in terms of dosage and medication choices), and the storage conditions for the frozen eggs.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding harmful habits like smoking and alcohol, and supplementing with antioxidant vitamins can also positively impact the chances of success.
How Long Can I Store My Eggs?
There is no definitive limit on how long eggs can be stored. Studies have documented cases where eggs were thawed and used 15-20 years after freezing, resulting in successful live births. In our country, frozen eggs can be stored in IVF centers for a maximum of five years. Extending storage beyond five years requires authorization from the Ministry of Health. If storage for more than five years is desired, an application can be submitted to the Ministry to request an extension.
Each year, the woman must submit a signed request indicating her desire to continue storing her frozen eggs. If this request is not submitted, a committee established by the health directorate may decide to destroy the eggs after a one-month period. This means you can thaw and use your eggs even after 10 years. The length of time eggs are frozen does not affect the chances of success once they are thawed.
Can Anyone Freeze Their Eggs?
In our country, women can freeze their eggs only under certain medical indications. Egg freezing cannot be performed on request for social reasons. In some other countries, however, any woman can choose to freeze her eggs. Here, women must obtain a report signed by three physicians prior to the egg freezing procedure. Any woman who obtains this report is eligible to freeze her eggs.
Can Married Women Freeze Eggs?
Married women who have not given birth can freeze their eggs. Married women can also freeze their eggs under the conditions set out in the regulation published by the ministry of health in 2014: before treatments that may damage the ovarian reserve, such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Before operations that may damage reproductive function (removal of the ovaries or operations that will damage the ovarian reserve), they may freeze their eggs if they have a low ovarian reserve and have not yet given birth, or if the family history of early menopause has been documented by a health board report consisting of at least three specialist doctors.


What are the Causes of Egg Laziness?
The reasons for egg laziness can be listed as follows.
- Genetic diseases; syndromes such as Turner syndrome, Fragil X....
- Family history of early menopause (mother and sisters, presence of early menopause in aunts)
- Smoking
- Consumption of alcohol
- After surgery (ovarian cyst operations, removal of ovaries)
- After chemotherapy treatment
- After radiotherapy treatment
- Endometriosis disease (Chocolate cysts; endometrioma)
How is Egg Freezing Performed in Istanbul?
Egg collection in Istanbul is done in 4 stages.
- First interview and examination
- Stimulation of eggs
- Collection of eggs
- Freezing of eggs
1. First Interview and Examination:
The patient's general condition, blood pressure, fever and pulse, weight and body mass index are evaluated.
First, the patient's history is taken;
A physical examination of the patient is performed.
If there is a short stature and a mane neck, Turner syndrome can be considered. The development of secondary sex characteristics should be checked; breast development, hair growth problems can be examined. Then a gynecological examination is performed; vaginal discharge and infection should be checked. The uterus and vagina should be evaluated for cervical anomalies. If necessary, a Pap smear test should be taken.
Ovarian reserve tests (AMH, FSH, ESTRADIOL) and infectious disease screening tests should be performed.
2. Stimulation of Eggs:
After the woman's history is taken and an examination is performed, the follicles (the sacs in which the egg develops and that we see on ultrasound) are enlarged for an average of 7-10 days with needle and pill treatments given on the 2nd or 3rd day of the menstrual period and their growth is monitored with ultrasound. The aim is to enlarge the maximum number of eggs. After the follicles reach a certain size (average diameter of 17-20 mm), a cracking needle is given and the egg collection process is performed 34-36 hours later.
3. Egg Collection:
In the IVF center, the patient is placed in a fork position called lithotomy under anesthesia, and the eggs are collected by passing through the vagina with the help of a needle inserted into the vaginal ultrasound probe. The collected eggs are delivered to the embryologist. The collected mature eggs are frozen.
The egg collection process (OPU) takes approximately 10-15 minutes. Afterwards, when the patient wakes up, they are taken from their room to their bed and rested for a while. Then they are discharged.
What are the Egg Freezing Techniques?
- Slow freezing
- Vitrification method: This is our preferred method. It is a fast freezing method. It is frozen at -196 degrees using liquid nitrogen. The formation of ice crystals is prevented by using substances called cryoprotectants. Frozen eggs can be stored in storage tanks for years, preserving their vitality.
How is the Quality of Eggs Determined?
Before the treatment, we can have preliminary information about the number of eggs (ovarian reserve) by checking the FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) or AMH (antimüllerian hormone, can be checked regardless of the day of the period) on the 2nd or 3rd day of the menstrual period or by counting the follicles with ultrasound. The collected eggs are examined under a microscope and it is decided whether they are mature or not. The mature, high-quality eggs are frozen for future use.
Advantages of Egg Freezing Procedure
The purpose of egg freezing is to protect women's fertility. Women's fertility decreases after the age of 35, so it increases the chances of women who are planning to have children at an older age to become mothers.
As age increases, the quality of eggs decreases, so the chance of getting pregnant or having a healthy baby decreases in later ages. Eggs that are frozen and stored are young eggs and are not affected by advancing age. Therefore, when young eggs frozen at an older age are used, the chance of having a healthy baby (low probability of chromosomal anomalies) increases.
Another advantage is that it allows women who will undergo cancer treatment to get pregnant in the future without being affected by the treatment. Eggs do not remain healthy with cancer treatment, so if we freeze eggs before treatment, we provide the woman with the chance of pregnancy with these healthy eggs in the future.
Women with a family history of early menopause are also at risk of early menopause, so they can get stressed about getting married and having children as soon as possible. Knowing that women in this situation have egg freezing options can reduce their stress and give them the chance to have children in the future.
Egg Freezing Prices
Egg freezing prices 2024 vary depending on how, why and under what conditions the procedure will be performed. At the same time, it may differ depending on the health status and condition of the person whose eggs will be frozen. Therefore, a detailed examination should be performed and a decision should be made accordingly. In short, a detailed examination should be performed in order for the prices to be determined. The stages required for the egg freezing procedure and the tests performed will affect the price. You can contact Assoc. Prof. Dr. Çiğdem Yayla Abide for the Istanbul egg freezing fee and learn whether you are a suitable candidate for this procedure with an examination.
In order to protect women's fertility, women can freeze their eggs and store them for at least 5 years under special conditions specified in the regulation published by the Ministry of Health in 2014. They can freeze eggs under the conditions set forth in the regulation published by the Ministry of Health in 2014. For single women who do not want to lose their virginity, eggs can be collected from the abdomen with an ultrasound under anesthesia. However, since the risk of organ injury is higher, the first choice is to collect the eggs vaginally. Egg freezing at a young age involves less medical treatment, more eggs collected, and an increased live birth rate. Eggs frozen with the vitrification method prevent ice crystals from forming in the cells and can be stored for years without damaging the cells. A decision is made on which patient the procedure will be applied to or not as a result of the examinations. In addition, the person must have certain conditions in order for this procedure to be applied. The method, which was first applied to cancer patients, is also applied to people with low egg reserve. Generally speaking, it cannot be done optionally. We do not recommend egg freezing to women who have gone through menopause or to women whose egg capacity has decreased significantly. With developing technology, successful results have been increasing in recent years. Studies have shown that the number of live births obtained from frozen and thawed eggs or embryos obtained from fresh eggs are similar. Women are born with a certain egg reserve. After puberty, this egg pool gradually decreases and after the age of 35, this decrease accelerates. Therefore, the chance of pregnancy decreases gradually after the age of 35. The freezing and storage of eggs and the thawing of frozen eggs to use them in the future to have children are done to preserve fertility. Egg freezing is done to preserve the fertility of the woman. Egg freezing or ovarian freezing are different procedures. In egg freezing, the eggs in the ovaries are frozen, while in ovarian freezing, the ovaries or a part of the ovaries can be surgically removed and the freezing process can be performed. The ovary is an organ medically called ovary. There are two ovarian tissues in a woman. There are also sacs called follicles inside the ovaries. There are eggs (the medical equivalent of eggs is oocytes) inside these sacs. We often perform egg freezing in our country. Therefore, when talking about the procedure, the correct one is egg freezing. Egg collection can be performed on virgins in two ways. The first is a procedure performed with abdominal ultrasound and needle, which does not break the woman's virginity; the second is a procedure performed with vaginal ultrasound and needle, which breaks the woman's virginity. There is no upper age limit for egg freezing, but we prefer to perform egg freezing under the age of 40. As age increases, the number of eggs decreases, the quality of the eggs also decreases, and genetic problems may occur. Therefore, egg freezing under the age of 40 is our preference.Is Egg Freezing Legal in Turkey?
Can Single Women Freeze Eggs?
How is Egg Collection Performed in Singles?
What is the Advantage of Egg Freezing at an Early Age?
Does Egg Freezing Damage Eggs?
Who are the Candidates for Egg Freezing?
Who Cannot Have Egg Freezing?
Can Egg Freezing Be Performed on Women with Low Ovarian Reserve?
Why is Egg Freezing Done?
Are egg freezing and ovarian freezing the same?
How is egg collection performed on virgins?
What is the age for ovarian freezing?